Cloud computing continues to transform the way organizations arethe doing business, proving to be a transformative innovation for many enterprises. It allows businesses to streamline their operations and develop more eco-friendly strategies, and, cloud-based systems have consistently proven to be more reliable and cost-efficient than in-house infrastructures. COVID time confirmed the benefits and importance of cloud computing with multiple folds of increase in demand for cloud services. [1]
By end of 2023, cloud computing is expected to become a $500 billion industry, and for good reason — whether users are on a desktop computer or mobile device, the cloud provides instant access to data anytime, anywhere there is an Internet connection. For businesses, cloud computing also offers myriad benefits, such as scalable storage for files, applications, and other types of data; improved collaboration regardless of team members’ locations; and saved time and money. [1]

Considering how far the cloud has come in recent years spurs questions of what kind of risks facing businesses when using Cloud Computing, the following list can help:
Risks from the perspective of the providers
- Security and privacy — data integration and ownership concerns persist. These concerns need to be addressed for the protection of intellectual property, employee, customer, and partner information.
- Governance — without oversight business leaders will be able to create shadow IT components or entire organizations. And within IT there are fewer barriers to creating unapproved environments.
- Regulatory — ensuring compliance with the myriad of rules including SOX, HIPAA, PCI, and others while taking advantage of the economic model.
- Staff — cloud expertise will be difficult to keep as more companies jump on the bandwagon and want to profit from the price paid by early adopters. [1]
Risks from the perspective of the customers
- Multitenancy (Shared Access): The problem with shared access is that there is a risk that your company’s sensitive data could accidentally show up in someone else’s space.
- Network Availability: When you work from the cloud, you are at the mercy of its availability. This means that if your provider’s systems go down, so do your access and productivity.
- Ownership of Data: Before you upload any files to the cloud, double-check your contract to make sure your property remains your property.
- Data Integrity: If you think that your data security is questionable when you store it on-site, imagine the risk when your data is being stored at a location you don’t even know.
- Cyberattacks Any time you store data on the Internet, you are at risk for a cyberattack. This is particularly problematic in the cloud, where volumes of data are stored by all types of users on the same cloud system. [1]

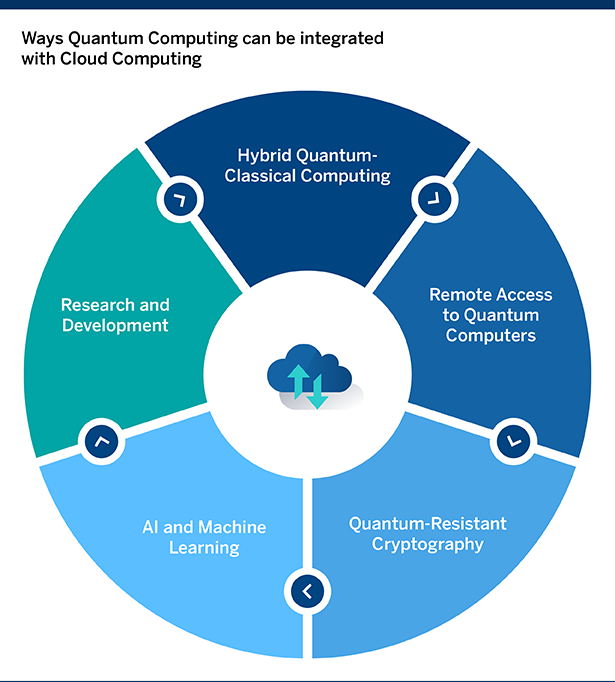
Ways Quantum Computing can be integrated with Cloud Computing
- Remote Access to Quantum Computers: By providing remote access to quantum computers, cloud computing can make quantum computing more accessible to a wider range of users. This can include researchers, developers, and businesses that may not have the resources or expertise to build and maintain their quantum computing infrastructure.
- Hybrid Quantum-Classical Computing: The combination of quantum and classical computing can offer significant performance benefits for certain types of computations. Cloud computing can provide the necessary classical computing resources to support these hybrid computations.
- Quantum-Resistant Cryptography: As quantum computers become more powerful, they will eventually be able to break many of the classical cryptographic algorithms that are currently in use. Cloud computing providers can use quantum computing to develop and implement quantum-resistant cryptography, ensuring the security of sensitive data stored in the cloud.
- AI and Machine Learning: By integrating quantum computing with AI and machine learning algorithms running in the cloud, it’s possible to solve complex optimization problems and make predictions with higher accuracy. For example, quantum computing can be used to improve the training of machine learning models or to search large datasets more efficiently.
- Research and Development: Cloud computing can support the development of new quantum algorithms and applications by providing researchers and developers with access to quantum hardware and computational resources. This can accelerate the pace of innovation in quantum computing and lead to breakthroughs and discoveries. [2]
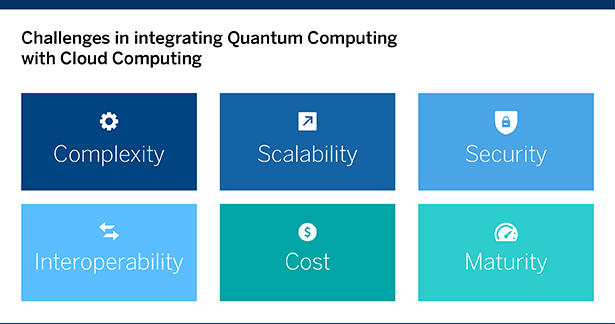
Challenges in integrating Quantum Computing with Cloud Computing
- Complexity: Quantum computing is a highly complex field that requires specialized knowledge and expertise to work with. This complexity can make it difficult for users to access and utilize quantum computing resources in the cloud.
- Scalability: Scalability is a challenge for both quantum and classical computing. However, integrating quantum computing with cloud computing adds additional challenges, such as the need for high-speed and low-latency communication between quantum and classical components, as well as the need to manage and allocate resources dynamically.
- Security: The integration of quantum computing with cloud computing raises new security concerns, such as the need to protect sensitive quantum algorithms and data from unauthorized access or tampering.
- Interoperability: As the field of quantum computing evolves, there may be a need for interoperability between different quantum computing technologies and platforms. This can be challenging, as different platforms may use different technologies and programming models.
- Cost: Implementing a quantum computing infrastructure, including the necessary hardware and software, can be expensive. Cloud computing can provide a more cost-effective alternative, but the costs of accessing and utilizing quantum computing resources in the cloud can still be high for some users.
- Maturity: Quantum computing is still a relatively new and rapidly evolving field, and many of the technologies and applications are still in the early stages of development. This can make it difficult to predict the future development of quantum computing and its integration with cloud computing. [2]
Requirements for using Quantum Computing in Cloud Computing
- Quantum Hardware: Access to quantum hardware, such as quantum processors or quantum simulators, is necessary for executing quantum algorithms and simulations. This hardware may be provided by cloud computing providers or may need to be procured by the user.
- Network Connectivity: High-speed and low-latency network connectivity is required to support remote access to quantum computing resources in the cloud. This can include both local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs).
- Quantum Software: A variety of quantum software tools and libraries may be needed to support the development and execution of quantum algorithms and simulations. This can include quantum compilers, quantum simulators, quantum programming languages, and quantum libraries.
- Security: Strong security measures are necessary to protect sensitive quantum algorithms and data from unauthorized access or tampering. This can include encryption, authentication, and access control mechanisms.
- Scalability: The integration of quantum computing with cloud computing must be scalable to support the needs of a wide range of users and applications. This can include the ability to dynamically allocate and manage computational resources and the ability to support high-performance computations.
- Interoperability: Interoperability between different quantum computing technologies and platforms is important to ensure compatibility and ease of use. This can include the use of common programming models and interfaces. [2]
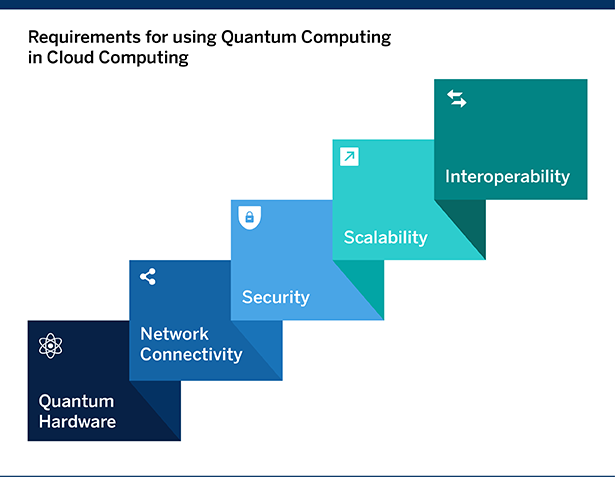
In conclusion, the integration of quantum computing with cloud computing requires access to quantum hardware, strong network connectivity, quantum software tools, security measures, scalability, interoperability, and cost-effectiveness, this will insure harnessing the max benefits of using quantum computing and utilizing the power and abilities provided by this disruptive technology. [2]
Ahmed Banafa, Author of the Books:
Secure and Smart Internet of Things (IoT) Using Blockchain and AI
Blockchain Technology and Applications
Quantum Computing
References
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/20140824000956-246665791-risks-of-cloud-computing-explained-both-sides/
Comments on this publication